From:
https://www.gartner.com/en/articles/what-s-new-in-the-2022-gartner-hype-cycle-for-emerging-technologies
August 10, 2022 Contributor: Lori Perri
Emerging technologies for 2022 fit into three main themes: evolving/expanding immersive experiences,
accelerated artificial intelligence automation, and optimized technologist delivery.
In short:
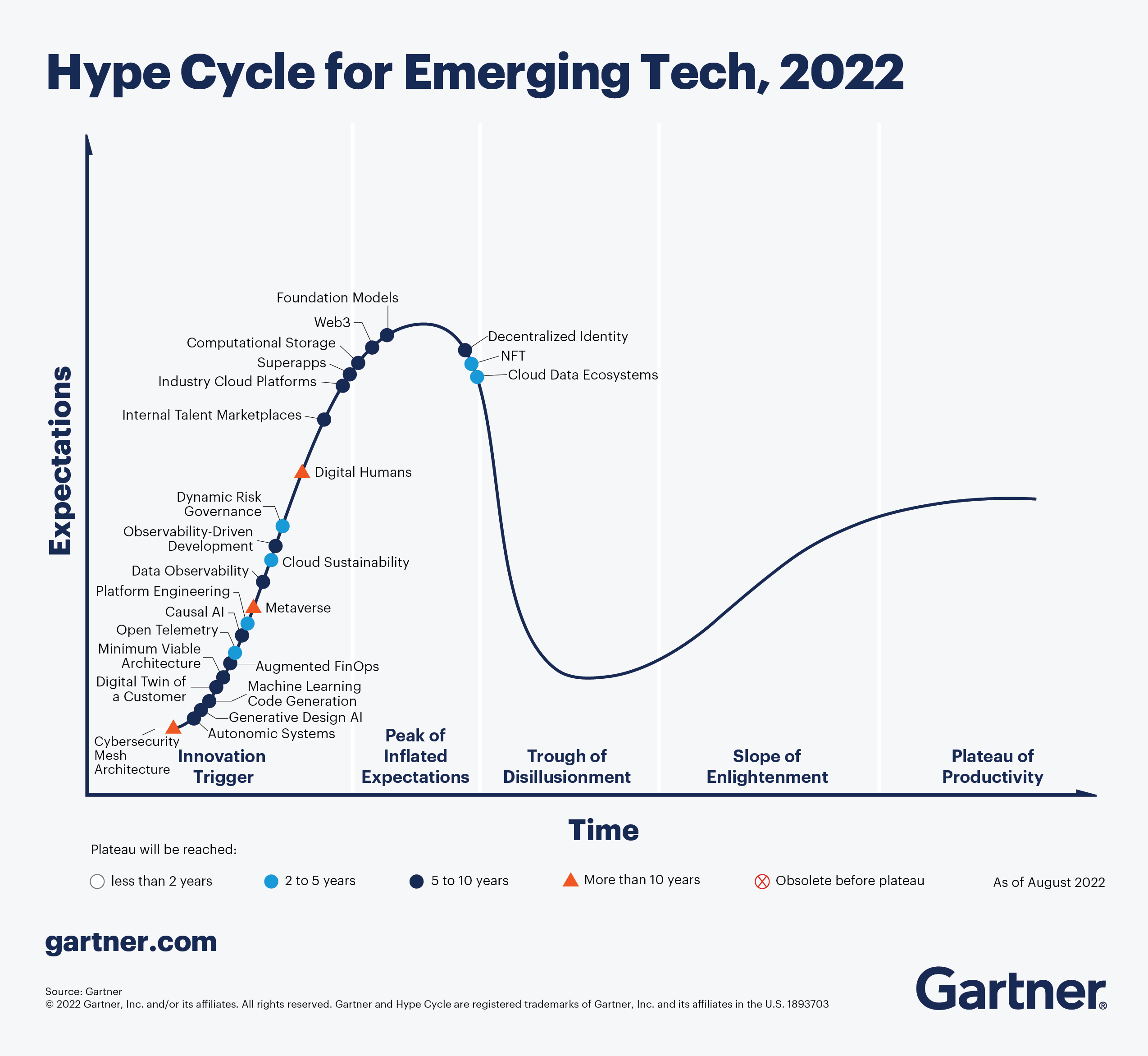
- The 2022 Gartner Hype Cycle™ for Emerging Technologies features 25 “must-know” innovations to drive competitive differentiation and efficiency.
- Only a few are likely to reach mainstream adoption in as little as two years; many will take 10 years or more.
- he embryonic nature of the technologies makes them more risky to deploy, but the benefits for early adopters are potentially greater.
- Expand immersive experiences
- Accelerate artificial intelligence (AI) automation
- Optimize technologist delivery
These technologies are expected to greatly impact business and society over the next two to 10 years, but will especially enable CIOs and IT leaders to deliver on digital business transformation.
Emerging technologies are disruptive by nature, without a well-known or proven competitive advantage. To capture the opportunities, it’s critical to understand the potential use cases and the technologies’ paths to mainstream adoption — which can be as little as two years or as long as 10 years or more.
“All these technologies are at an early stage, but some are at an embryonic stage, and great uncertainty exists about how they will evolve. The embryonic technologies present greater risks for deployment but potentially greater benefits for early adopters, which differentiates them from Gartner’s top strategic technology trends,” says Melissa Davis, VP Analyst at Gartner.
Three Hype Cycle themes to think aboutin 2022 and beyond
The 2022 Gartner Hype Cycle featuresemerging technologies and distills insights from more than 2,000 technologiesinto a succinct high-potential set. Most technologies have multiple use casesbut enterprise architecture and technology innovation leaders should prioritizethose with the greatest potential benefit for their organization. (They willalso need to launch a proof-of-concept project to demonstrate the feasibilityof a technology for their target use case.)
2021-2023 Emerging Technology Roadmap for Large Enterprises
Here’s more about the three themes underwhich the 2022 technologies fall:
Theme 1: Evolving/expanding immersiveexperiences
The benefit of these technologies is thatthey provide individuals with more control over their identities and data, andexpand their range of experiences into virtual venues and ecosystems that canbe integrated with digital currencies. These technologies also provide new waysto reach customers to strengthen or open up new revenue streams.
Digital twin of the customer (DToC) is adynamic virtual representation of a customer that simulates and learns toemulate and anticipate behavior. It can be used to modify and enhance thecustomer experience (CX) and support new digitalization efforts, products,services and opportunities. DToC will take five to 10 years until mainstreamadoption but will be transformational to organizations.
Other critical technologies in immersiveexperiences include the following:
· Decentralized identity (DCI) allows an entity (typically ahuman user) to control their own digital identity by leveraging technologiessuch as blockchain or other distributed ledger technologies (DLTs), along withdigital wallets.
· Digital humans are interactive, AI-drivenrepresentations that have some of the characteristics, personality, knowledgeand mindset of a human.
· Internal talent marketplaces match internal employees and, insome cases, a pool of contingent workers, to time-boxed projects and variouswork opportunities, with no recruiter involvement.
· Metaverse is a collective virtual 3D sharedspace, created by the convergence of virtually enhanced physical and digitalreality. A metaverse is persistent, providing enhanced immersive experiences.
· Non-fungibletoken (NFT) is a unique programmable blockchain-based digital item thatpublicly proves ownership of digital assets, such as digital art or music, orphysical assets that are tokenized, such as houses, cars or documents.
· Superapp is a composite mobile app built as a platformto deliver modular microapps that users can activate for personalized appexperiences.
· Web3 is a new stack of technologies forthe development of decentralized web applications that enable users to controltheir own identity and data.
Theme 2: Accelerated AI automation
Expanding AI adoption is a critical way toevolve products, services and solutions. It means accelerating the creation ofspecialized AI models, applying AI to the development andtraining of AI models, and deploying them to product, service and solutiondelivery. Outcomes include more accurate predictions and decisions and thefaster capture of expected benefits. The role of humans is also more focused onbeing consumers, assessors and overseers.
Autonomic systems are examples ofaccelerated AI automation. They are self-managing physical or software systems,performing domain-bounded tasks that exhibit three fundamental characteristics:autonomy, learning and agency. When traditional AI techniques aren’t ableto achieve business adaptability, flexibility and agility, autonomicsystems can be successful in helping with implementation. Autonomic systemswill take five to 10 years until mainstream adoption but will betransformational to organizations.
Other critical technologies in acceleratedAI automation include the following:
· Causal artificial intelligence (AI) identifies and utilizes cause-and-effectrelationships to go beyond correlation-based predictive models and toward AIsystems that can prescribe actions more effectively and act more autonomously.
· Foundation models are transformer architecture-basedmodels, such as large language models, which embody a type of deep neuralnetwork architecture that computes a numerical representation of text in thecontext of surrounding words, emphasizing sequences of words.
· Generative design AI or AI-augmented design, is the useof AI, machine learning (ML) and natural language processing (NLP) technologiesto automatically generate and develop user flows, screen designs, content, andpresentation-layer code for digital products.
· Machine learning code generation tools include cloud-hosted ML modelsthat plug into professional developer integrated development environments(IDEs), which are extensions that provide suggested code based on eithernatural language descriptions or partial code fragments.
Theme 3: Optimized technologist delivery
These technologies focus on key constituentsin building a digital business: product, service or solution buildercommunities (like fusion teams) and the platforms they use. Thesetechnologies provide feedback and insight that optimize and accelerate product,service and solution delivery and increase sustainability of businessoperations.
Cloud data ecosystems exemplify optimizedtechnologist delivery. They provide a cohesive data management environment thatably supports the whole range of data workloads, from exploratory data scienceto production data warehousing. Cloud data ecosystems provide streamlineddelivery and comprehensive functionality that is straightforward to deploy,optimize and maintain. They will take two to five years until mainstreamadoption and will be highly beneficial to users.
Other critical technologies in optimizedtechnologist delivery include the following:
· Augmented FinOps automates traditional DevOpsconcepts of agility, continuous integration and deployment, and end-userfeedback to financial governance, budgeting and cost optimization effortsthrough the application of AI and machine learning (ML) practices.
· Cloud sustainability is the use of cloud services toachieve sustainability benefits within economic, environmental and socialsystems.
· Computational storage (CS) offloads host processing from the main memoryof the central processing unit (CPU) to the storage device.
· Cybersecurity mesharchitecture (CSMA) is an emerging approach for architecting composable,distributed security controls that improve overall security effectiveness.
· Data observability is the ability to understand thehealth of an organization’s data landscape, data pipelines and datainfrastructure by continuously monitoring, tracking, alerting, analyzing andtroubleshooting incidents.
· Dynamic riskgovernance (DRG) is a new approach to the critical task of defining theroles and responsibilities for risk management. DRG customizes risk governanceappropriately to each risk, enabling organizations to better manage risks andlower the cost of assurance.
· Industry cloud platforms leverage underlying SaaS, platformas a service (PaaS) and infrastructure as a service (IaaS) cloud services tooffer industry-relevant packaged business and technical capabilities to anidentified vertical as a whole product offering.
· Minimum viable architecture (MVA) is a standardized frameworkused by product teams to ensure the timely and compliant development, anditeration, of products.
· Observability-driven development (ODD) is a software engineeringpractice that provides fine-grained visibility and context into system stateand behavior by designing systems to be observable.
· OpenTelemetry is a collection of specifications,tools, application programming interfaces (APIs) and software development kits(SDKs) that describe and support the implementation of an open-sourceinstrumentation and observability framework for software.
· Platform engineering is the discipline of building andoperating self-service internal developer platforms (IDPs) for softwaredelivery and life cycle management.

